正在载入交互式动画窗口请稍等
稀疏矩阵-三元组 可视化交互式动画版

如果矩阵中的大多数元素为零,则该矩阵称为稀疏矩阵。 将零元素存储在矩阵中是浪费的,因为它们不会影响我们的计算结果。 这就是为什么我们以比标准二维数组更有效的表示形式来实现这些矩阵。 使用更有效的表示,我们可以显着降低操作的空间和时间复杂性。
我们在以下文章中讨论了 4 种不同的表示形式:
- 稀疏矩阵表示| 套装1
- 稀疏矩阵表示| 设置 2 。
在本文中,我们将讨论稀疏矩阵的另一种表示形式,通常称为耶鲁格式。
CSR
(压缩稀疏行)或耶鲁格式
类似于稀疏矩阵的数组表示(在第 1 组中讨论)。
我们用三个称为 A、IA、JA 的一维数组或向量来表示矩阵 M (m * n)。
令
NNZ
表示 M 中非零元素的数量,并注意使用基于 0 的索引。
- A 向量的大小为 NNZ,它存储矩阵非零元素的值。 值按照逐行遍历矩阵的顺序出现
-
IA 向量的大小为 m+1,存储直到(不包括)第 i 行的非零元素的累积数量。
它由递归关系定义:
- IA[0] = 0
- IA[i] = IA[i-1] + 矩阵第 (i-1) 行中非零元素的数量
- JA向量存储A向量中每个元素的列索引。 因此它的大小也是 NNZ。
为了找到第 i 行中非零元素的数量,我们执行 IA[i+1] – IA[i]。
请注意此表示与基于数组的实现有何不同,其中第二个向量存储非零元素的行索引。
以下示例显示了如何表示这些矩阵。
例子:
输入:0 0 0 0 5 8 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 6 0 0 解决方案:当逐行读取矩阵时 行,A 向量为 [ 5 8 3 6] JA向量存储列索引 A 中的元素数,因此 JA = [ 0 1 2 1]。IA[0] = 0。IA[1] = IA[0] + 无 第 0 行中的非零元素数 即 0 + 0 = 0。 相似地, IA[2] = IA[1] + 2 = 2 IA[3] = IA[2] + 1 = 3 IA[4] = IA[3]+1 = 4 因此 IA = [0 0 2 3 4] 诀窍是记住 IA[i] 存储 NNZ 最多且不包括 我划船。 输入:10 20 0 0 0 0 0 30 0 4 0 0 0 0 50 60 70 0 0 0 0 0 0 80 输出:A = [10 20 30 4 50 60 70 80], IA = [0 2 4 7 8] JA = [0 1 1 3 2 3 4 5]
算法:
稀疏(矩阵) 步骤 1:将 M 设置为 MATRIX 中的行数 步骤 2:将 N 设置为 MATRIX 中的列数 步骤 3:I = 0,NNZ = 0。声明 A、JA 和 IA。 将 IA[0] 设置为 0 步骤 4:对于 I = 0 ... N-1 步骤 5:对于 J = 0 ... N-1 步骤 5:如果 MATRIX [I][J] 不为零 将矩阵 [I][J] 添加到 A 将 J 添加到 JA NNZ = NNZ + 1 [如果结束] 第6步:[J循环结束] 将 NNZ 添加到 IA [ I 循环结束 ] 步骤7:打印向量A、IA、JA 第 8 步:结束
执行:
消费者保护计划
// CPP program to find sparse matrix rep-// resentation using CSR#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;typedef std::vector<int> vi;typedef vector<vector<int> > matrix;// Utility Function to print a Matrixvoid printMatrix(const matrix& M){ int
m = M.size();
int
n = M[0].size();
for
(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) cout << M[i][j] << " "; cout << endl; }}// Utility Function to print A, IA, JA vectors// with some decoration.
void printVector(const vi& V, char* msg){ cout << msg << "[ "; for_each(V.begin(), V.end(), [](int
a) {
cout << a << " "; }); cout << "]" << endl;}// Generate the three vectors A, IA, JA void sparesify(const matrix& M){ int
m = M.size();
int
n = M[0].size(), i, j;
vi A; vi IA = { 0 }; // IA matrix has N+1 rows
vi JA;
int
NNZ = 0;
for
(i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (M[i][j] != 0) { A.push_back(M[i][j]); JA.push_back(j); // Count Number of Non Zero // Elements in row i NNZ++; } } IA.push_back(NNZ); } printMatrix(M); printVector(A, (char*)"A = "); printVector(IA, (char*)"IA = "); printVector(JA, (char*)"JA = ");}// Driver codeint main(){ matrix M = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 }, { 5, 8, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 3, 0, 0 }, { 0, 6, 0, 0, 1 }, }; sparesify(M); return 0;} |
Java
import java.util.*;// Java program to find sparse matrix// resentation using CSRpublic class GFG { // Utility Function to print a Matrix private
static void printMatrix(int[][] M)
{ int m = M.length; int n = (M.length == 0 ? 0 : M[0].length);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.print(M[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } // Utility Function to print A, IA, JA vectors // with some decoration. private
static void printVector(ArrayList<Integer> V,
String msg) { System.out.print(msg + "[ "); for (var a : V) { System.out.print(a + " "); } System.out.println("]"); } // Generate the three vectors A, IA, JA private
static void sparesify(int[][] M)
{ int m = M.length; int n = (M.length == 0 ? 0 : M[0].length), i, j; ArrayList<Integer> A = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList<Integer> IA = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // IA matrix has N+1 // rows ArrayList<Integer> JA = new ArrayList<Integer>(); int NNZ = 0; for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (M[i][j] != 0) { A.add(M[i][j]); JA.add(j); // Count Number of Non Zero // Elements in row i NNZ++; } } IA.add(NNZ); } printMatrix(M); printVector(A, "A = "); printVector(IA, "IA = "); printVector(JA, "JA = "); } // Driver code public
static void main(String[] args)
{ int[][] M = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 }, { 5, 8, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 3, 0, 0 }, { 0, 6, 0, 0, 1 } }; // Function call sparesify(M); }}// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi |
C#
// C# program to find sparse matrix// resentation using CSRusing System;using System.Collections.Generic;class GFG { // Utility Function to print a Matrix static
void printMatrix(int[, ] M)
{ int m = M.GetLength(0); int n = M.GetLength(1); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) Console.Write(M[i, j] + " "); Console.WriteLine(); } } // Utility Function to print A, IA, JA vectors // with some decoration. static
void printVector(List<int> V, string msg)
{ Console.Write(msg + "[ "); foreach(var
a in V) { Console.Write(a + " "); }
Console.WriteLine("]"); } // Generate the three vectors A, IA, JA static
void sparesify(int[, ] M)
{ int m = M.GetLength(0); int n = M.GetLength(1), i, j; List<int> A = new List<int>(); List<int> IA = new List<int>(); // IA matrix has N+1 rows List<int> JA = new List<int>(); int NNZ = 0; for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (M[i, j] != 0) { A.Add(M[i, j]); JA.Add(j); // Count Number of Non Zero // Elements in row i NNZ++; } } IA.Add(NNZ); } printMatrix(M); printVector(A, "A = "); printVector(IA, "IA = "); printVector(JA, "JA = "); } // Driver code public
static void Main()
{ int[, ] M = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 }, { 5, 8, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 3, 0, 0 }, { 0, 6, 0, 0, 1 }, }; // Function call sparesify(M); }}// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi |
Python3
# Python 3 program to find sparse matrix# resentation using CSRclass GFG : # Utility Function to print a Matrix @staticmethod def printMatrix( M) : m = len(M) n = (0 if len(M) == 0 else len(M[0])) i = 0 while (i < m) : j = 0 while (j < n) : print(str(M[i][j]) + " ", end ="") j += 1 print() i += 1 # Utility Function to print A, IA, JA vectors # with some decoration. @staticmethod def printVector( V, msg) : print(msg +
"[ ", end ="")
for a in V : print(str(a) +
" ", end ="")
print("]") # Generate the three vectors A, IA, JA @staticmethod def sparesify( M) : m = len(M) n = (0 if len(M) == 0 else len(M[0])) i = 0 j = 0 A = []
IA = []
# IA matrix has N+1 # rows JA = []
NNZ = 0 i = 0 while (i < m) : j = 0 while (j < n) : if (M[i][j] !=
0) :
A.append(M[i][j]) JA.append(j) # Count Number of Non Zero # Elements in row i NNZ += 1 j += 1 IA.append(NNZ) i += 1 GFG.printMatrix(M) GFG.printVector(A, "A = ") GFG.printVector(IA, "IA = ") GFG.printVector(JA, "JA = ") # Driver code @staticmethod def main( args) : M = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 1], [5, 8, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 3, 0, 0], [0, 6, 0, 0, 1]] # Function call GFG.sparesify(M) if __name__=="__main__": GFG.main([]) |
JavaScript
// JS program to find sparse matrix// resentation using CSRclass GFG{ // Utility Function to print a Matrix printMatrix( M) { let m = M.length let n = (m == 0) ? 0 : M[0].length let i = 0 while (i < m) { let j = 0 while (j < n) { process.stdout.write((M[i][j]) + " ") j += 1 } console.log() i += 1 } } // Utility Function to print A, IA, JA vectors // with some decoration. printVector( V, msg) { process.stdout.write(msg + "[ ") process.stdout.write(V.join(" ") ) console.log("]")
} // Generate the three vectors A, IA, JA sparesify( M) { let m = M.length let n = (m == 0) ? 0 : M[0].length let j = 0 let A = [] let IA = [] // IA matrix has N+1 // rows let JA = [] let NNZ = 0 let i = 0 while (i < m) { j = 0 while (j < n) { if (M[i][j] != 0) { A.push(M[i][j]) JA.push(j) // Count Number of Non Zero // Elements in row i NNZ += 1 } j += 1 } IA.push(NNZ) i += 1 } g.printMatrix(M) g.printVector(A, "A = ") g.printVector(IA, "IA = ") g.printVector(JA, "JA = ") }}// Driver codelet M = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 1], [5, 8, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 3, 0, 0], [0, 6, 0, 0, 1]]
// Function calllet g = new GFG()g.sparesify(M) // This code is contributed by phasing17. |
0 0 0 0 1 5 8 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 6 0 0 1 A = [ 1 5 8 3 6 1 ] IA = [ 0 1 3 4 6 ] JA = [ 4 0 1 2 1 4 ]
时间复杂度:
O(nxm)
辅助空间:O(n + m)
笔记
- 矩阵的稀疏性 = ( 元素总数 – 非零元素数) / ( 元素总数) 或 (1 – NNZ/mn ) 或 ( 1 – size(A)/mn ) 。
- 基于直接数组的表示需要 3 * NNZ 内存,而 CSR 需要 ( 2*NNZ + m + 1) 内存。
-
CSR 矩阵的内存效率只要
.
- 与 CSR 类似,还有 CSC,它代表压缩稀疏列。 它是 CSR 的类似物。
- “新”Yale 格式进一步将 A 和 JA 向量压缩为 1 个向量。
如果您喜欢 图码 并愿意做出贡献,您还可以使用 write.geeksforgeeks.org 撰写文章或将您的文章邮寄至 review-team@geeksforgeeks.org。 查看您的文章出现在 图码 主页上并帮助其他极客。
矩阵是由 m 行 和 n 列组成的二维数据对象,因此共有 mxn 值。 如果矩阵的大部分元素的 值为0 ,则称为稀疏矩阵。
为什么使用稀疏矩阵而不是简单矩阵?
- 存储: 非零元素比零少,因此可以使用更少的内存来仅存储这些元素。
- 计算时间: 通过逻辑设计仅遍历非零元素的数据结构可以节省计算时间。
例子:
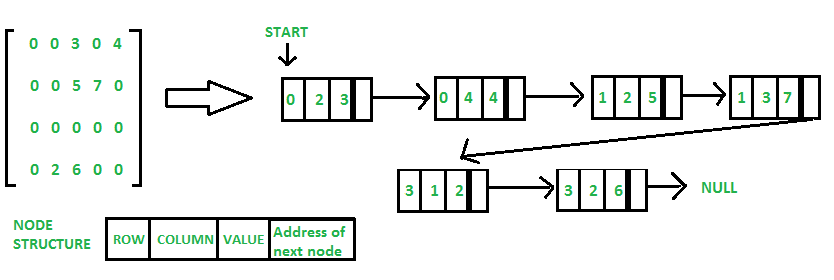
0 0 3 0 4
0
0 5 7 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 2 6 0 0
用二维数组表示稀疏矩阵会导致大量内存的浪费,因为矩阵中的零在大多数情况下没有用处。 因此,我们不存储带有非零元素的零,而是只存储非零元素。 这意味着用三元组(行、列、值)存储非零元素 。
稀疏矩阵表示可以通过多种方式完成,以下是两种常见的表示:
- 数组表示
- 链表表示
方法一:使用数组:
二维数组用于表示稀疏矩阵,其中有三行,名称为
- Row: 行的索引,非零元素所在的位置
- Column: 列的索引,非零元素所在的位置
- Value: 位于索引处的非零元素的值 - (行,列)

执行:
C++
// C++ program for Sparse Matrix Representation// using Array#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(){ // Assume 4x5 sparse matrix int
sparseMatrix[4][5] = { {0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 }, {0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 }, {0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, {0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 } }; int
size = 0; for
(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) size++; // number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be // equal to number of non - zero elements in // sparseMatrix int
compactMatrix[3][size]; // Making of new matrix int
k = 0; for
(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) { compactMatrix[0][k] = i; compactMatrix[1][k] = j; compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j]; k++; } for
(int i=0; i<3; i++) { for (int j=0; j<size; j++) cout <<" "<< compactMatrix[i][j]; cout <<"\n";
} return 0;}// this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
C
// C++ program for Sparse Matrix Representation// using Array#include<stdio.h>
int main(){ // Assume 4x5 sparse matrix int
sparseMatrix[4][5] = { {0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 }, {0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 }, {0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, {0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 } }; int
size = 0; for
(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) size++; // number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be // equal to number of non - zero elements in // sparseMatrix int
compactMatrix[3][size]; // Making of new matrix int
k = 0; for
(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) { compactMatrix[0][k] = i; compactMatrix[1][k] = j; compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j]; k++; } for
(int i=0; i<3; i++) { for (int j=0; j<size; j++) printf("%d ", compactMatrix[i][j]); printf("\n"); } return 0;} |
Java
// Java program for Sparse Matrix Representation// using Arrayclass GFG { public
static void main(String[] args) { int sparseMatrix[][] = { {0, 0, 3, 0, 4}, {0, 0, 5, 7, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 2, 6, 0, 0} }; int size = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) { size++; } } } // number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be // equal to number of non - zero elements in // sparseMatrix int compactMatrix[][] = new int[3][size]; // Making of new matrix int k = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) { compactMatrix[0][k] = i; compactMatrix[1][k] = j; compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j]; k++; } } } for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { System.out.printf("%d ", compactMatrix[i][j]); } System.out.printf("\n"); } }} /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */ |
Python3
# Python program for Sparse Matrix Representation# using arrays# assume a sparse matrix of order 4*5 # let assume another matrix compactMatrix # now store the value,row,column of arr1 in sparse matrix compactMatrix
sparseMatrix = [[0,0,3,0,4],[0,0,5,7,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,2,6,0,0]]# initialize size as 0size = 0for i in range(4): for j in range(5): if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0): size += 1# number of columns in compactMatrix(size) should# be equal to number of non-zero elements in sparseMatrixrows, cols = (3, size)compactMatrix = [[0 for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)]k = 0for i in range(4): for j in range(5): if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0): compactMatrix[0][k] = i compactMatrix[1][k] = j compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j] k += 1for i in compactMatrix: print(i)# This code is contributed by MRINALWALIA |
C#
// C# program for Sparse Matrix Representation// using Arrayusing System;class Program { static
void Main(string[] args) { // Assume 4x5 sparse matrix int[, ] sparseMatrix = new int[4, 5] { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } }; int size = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) size++; // number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be // equal to number of non - zero elements in // sparseMatrix int[, ] compactMatrix = new int[3, size]; // Making of new matrix int k = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) { compactMatrix[0, k] = i; compactMatrix[1, k] = j; compactMatrix[2, k] = sparseMatrix[i, j]; k++; } } for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) Console.Write(" " + compactMatrix[i, j]); Console.WriteLine(); } }}// This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420) |
JavaScript
//JS program for Sparse Matrix Representation// using Array // Assume 4x5 sparse matrix let sparseMatrix = [ [0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 ], [0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 ], [0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ], [0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 ] ]; let size = 0; for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (let j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) size++; // number of columns in compactMatrix (size) must be // equal to number of non - zero elements in // sparseMatrix let compactMatrix = new Array(3); for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) compactMatrix[i] = new Array(size); // Making of new matrix let k = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (let j = 0; j < 5; j++) if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) { compactMatrix[0][k] = i; compactMatrix[1][k] = j; compactMatrix[2][k] = sparseMatrix[i][j]; k++; } for (let i=0; i<3; i++) { for (let j=0; j<size; j++) process.stdout.write(" " + compactMatrix[i][j]); console.log() }// this code is contributed by phasing17 |
0 0 1 1 3 3 2 4 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 7 2 6
时间复杂度: O(NM),其中 N 是稀疏矩阵中的行数,M 是稀疏矩阵中的列数。
辅助空间: O(NM),其中N是稀疏矩阵的行数,M是稀疏矩阵的列数。
方法2:使用链表
在链表中,每个节点有四个字段。
这四个字段定义为:
- Row: 行的索引,非零元素所在的位置
- Column: 列的索引,非零元素所在的位置
- Value: 位于索引处的非零元素的值 - (行,列)
- 下一个节点: 下一个节点的地址
C++
// C++ program for sparse matrix representation.// Using Link list #include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Node class to represent link listclass Node{ public: int
row; int
col; int
data; Node *next;
};// Function to create new nodevoid create_new_node(Node **p, int row_index, int col_index, int x){ Node *temp = *p; Node *r;
// If link list is empty then // create first node and assign value. if
(temp == NULL) { temp = new Node(); temp->row = row_index; temp->col = col_index; temp->data = x; temp->next = NULL; *p = temp; } // If link list is already created // then append newly created node else
{ while (temp->next != NULL) temp = temp->next;
r = new Node(); r->row = row_index; r->col = col_index; r->data = x; r->next = NULL; temp->next = r; }}// Function prints contents of linked list// starting from startvoid printList(Node *start){ Node *ptr = start; cout << "row_position:"; while (ptr != NULL) { cout << ptr->row << " "; ptr = ptr->next; } cout << endl; cout << "column_position:"; ptr = start; while (ptr != NULL) { cout << ptr->col << " "; ptr = ptr->next; } cout << endl; cout << "Value:"; ptr = start; while (ptr != NULL) { cout << ptr->data << " "; ptr = ptr->next; }}// Driver Codeint main(){ // 4x5 sparse matrix int
sparseMatrix[4][5] = { { 0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 }, { 0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 } }; // Creating head/first node of list as NULL Node *first = NULL; for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
// Pass only those values which // are non - zero if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) create_new_node(&first, i, j, sparseMatrix[i][j]); } } printList(first); return 0;}// This code is contributed by ronaksuba |
C
// C program for Sparse Matrix Representation// using Linked Lists#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Node to represent sparse matrixstruct Node{ int
value; int
row_position; int
column_postion; struct Node *next;};// Function to create new nodevoid create_new_node(struct Node** start, int non_zero_element, int row_index, int column_index ){ struct Node *temp, *r; temp = *start; if
(temp == NULL) { // Create new node dynamically temp = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof(struct Node)); temp->value = non_zero_element; temp->row_position = row_index; temp->column_postion = column_index; temp->next = NULL; *start = temp; } else
{ while (temp->next != NULL) temp = temp->next; // Create new node dynamically r = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof(struct Node)); r->value = non_zero_element; r->row_position = row_index; r->column_postion = column_index; r->next = NULL; temp->next = r; }}// This function prints contents of linked list// starting from startvoid PrintList(struct Node* start){ struct Node *temp, *r, *s; temp = r = s = start; printf("row_position: "); while(temp != NULL) { printf("%d ", temp->row_position); temp = temp->next; } printf("\n"); printf("column_postion: "); while(r != NULL) { printf("%d ", r->column_postion); r = r->next; } printf("\n"); printf("Value: "); while(s != NULL) { printf("%d ", s->value); s = s->next; } printf("\n");}// Driver of the program
int main(){ // Assume 4x5 sparse matrix int
sparseMatric[4][5] = { {0 , 0 , 3 , 0 , 4 }, {0 , 0 , 5 , 7 , 0 }, {0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, {0 , 2 , 6 , 0 , 0 } }; /* Start with the empty list */ struct Node* start = NULL; for
(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) // Pass only those values which are non - zero if (sparseMatric[i][j] != 0) create_new_node(&start, sparseMatric[i][j], i, j); PrintList(start); return 0;} |
Java
// Java program for sparse matrix representation.// Using Link listimport java.util.*;public class SparseMatrix { // Creating head/first node of list as NULL static
Node first = null; // Node class to represent link list public
static class Node { int row; int col; int data; Node next; }; // Driver Code public
static void main(String[] args) { // 4x5 sparse matrix int[][] sparseMatrix = { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } }; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { // Pass only those values which // are non - zero if (sparseMatrix[i][j] != 0) { create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatrix[i][j]); } } } printList(first); } // Function to create new node private
static void create_new_node(int row_index, int col_index, int x)
{ Node temp = first; Node r; // If link list is empty then // create first node and assign value. if (temp == null) { temp = new Node(); temp.row = row_index; temp.col = col_index; temp.data = x; temp.next = null;
first = temp; } // If link list is already created // then append newly created node else { while (temp.next != null) temp = temp.next; r = new Node();
r.row = row_index; r.col = col_index; r.data = x; r.next = null;
temp.next = r; } } // Function prints contents of linked list // starting from start public
static void printList(Node start) { Node ptr = start; System.out.print("row_position:"); while (ptr != null) { System.out.print(ptr.row + " "); ptr = ptr.next; } System.out.println(""); System.out.print("column_position:"); ptr = start; while (ptr != null) { System.out.print(ptr.col + " "); ptr = ptr.next; } System.out.println(""); System.out.print("Value:"); ptr = start; while (ptr != null) { System.out.print(ptr.data + " "); ptr = ptr.next; } }}// This code is contributed by Tapesh (tapeshdua420) |
Python3
# Python Program for Representation of# Sparse Matrix using Linked List# Node Class to represent Linked List Nodeclass Node: # Making the slots for storing row, # column, value, and address __slots__ = "row", "col", "data", "next" # Constructor to initialize the values def __init__(self, row=0, col=0, data=0, next=None): self.row = row self.col = col self.data =
data self.next
= next# Class to convert Sparse Matrix# into Linked Listclass Sparse: # Initialize Class Variables def __init__(self):
self.head =
None self.temp =
None self.size =
0 # Function which returns the size # of the Linked List def __len__(self):
return self.size
# Check the Linked List is # Empty or not def isempty(self):
return self.size == 0 # Responsible function to create # Linked List from Sparse Matrix def create_new_node(self, row, col, data): # Creating New Node newNode = Node(row, col, data, None) # Check whether the List is # empty or not if self.isempty(): self.head =
newNode else: self.temp.next
= newNode self.temp =
newNode # Incrementing the size self.size += 1 # Function display the contents of # Linked List def PrintList(self):
temp = r = s = self.head print("row_position:", end=" ") while temp !=
None: print(temp.row, end=" ") temp = temp.next print() print("column_postion:", end=" ") while r !=
None: print(r.col, end=" ") r = r.next print() print("Value:", end=" ") while s !=
None: print(s.data, end=" ") s = s.next print()# Driver Codeif __name__ ==
"__main__": # Creating Object s = Sparse() # Assuming 4x5 Sparse Matrix sparseMatric = [[0, 0, 3, 0, 4], [0, 0, 5, 7, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 2, 6, 0, 0]] for i in range(4): for j in range(5): # Creating Linked List by only those # elements which are non-zero if sparseMatric[i][j] != 0: s.create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatric[i][j]) # Printing the Linked List Representation # of the sparse matrix s.PrintList() # This code is contributed by Naveen Rathore |
C#
// C# program for sparse matrix representation.// Using Link listusing System;class Program{
// Creating head/first node of list as NULL static
Node first = null; // Node class to represent link list public
class Node { public int row;
public int col;
public int data; public Node next; }; // Driver Code static
void Main(string[] args) { // 4x5 sparse matrix int[, ] sparseMatrix = { { 0, 0, 3, 0, 4 },
{ 0, 0, 5, 7, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 2, 6, 0, 0 } }; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { // Pass only those values which // are non - zero if (sparseMatrix[i, j] != 0) { create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatrix[i, j]); } } } printList(first); } // Function to create new node private
static void create_new_node(int row_index, int col_index, int x)
{ Node temp = first; Node r; // If link list is empty then // create first node and assign value. if (temp == null) { temp = new Node(); temp.row = row_index; temp.col = col_index; temp.data = x; temp.next = null;
first = temp; } // If link list is already created // then append newly created node else { while (temp.next != null) temp = temp.next; r = new Node();
r.row = row_index; r.col = col_index; r.data = x; r.next = null;
temp.next = r; } } // Function prints contents of linked list // starting from start public
static void printList(Node start) { Node ptr = start; Console.Write("row_position:"); while (ptr != null) { Console.Write(ptr.row + " "); ptr = ptr.next; } Console.WriteLine(""); Console.Write("column_position:"); ptr = start; while (ptr != null) { Console.Write(ptr.col + " "); ptr = ptr.next; } Console.WriteLine(""); Console.Write("Value:"); ptr = start; while (ptr != null) { Console.Write(ptr.data + " "); ptr = ptr.next; } }}// This code is contributed by Tapesh (tapeshdua420) |
JavaScript
// JS Program for Representation of// Sparse Matrix into Linked List// Node Class to represent Linked List Nodeclass Node{ constructor(row, col, data) { this.row = row; this.col = col; this.data = data; this.next = null; }}// Class to convert Sparse Matrix// into Linked Listclass Sparse{ // Initialize Class Variables constructor() { this.head = null this.temp = null this.size = 0 } // Function which returns the size // of the Linked List len() { return this.size } // Check the Linked List is // Empty or not isempty()
{ return this.size == 0 } // Responsible function to create // Linked List from Sparse Matrix create_new_node(row, col, data) { // Creating New Node let newNode = new Node(row, col, data) // Check whether the List is // empty or not if (this.isempty()) this.head = newNode else (this.temp).next = newNode this.temp = newNode // Incrementing the size this.size += 1 } // Function display the contents of // Linked List PrintList()
{ let temp = this.head let r = this.head
let s = this.head
process.stdout.write("row_position: ") while (temp != null) { process.stdout.write(temp.row + " ") temp = temp.next } console.log() process.stdout.write("column_postion: ") while (r != null) { process.stdout.write(r.col + " " ) r = r.next } console.log() process.stdout.write("Value: ") while (s != null) { process.stdout.write(s.data + " ") s = s.next } console.log() }}// Driver Code// Creating Objectlet s = new Sparse()// Assuming 4x5 Sparse Matrixlet sparseMatric = [[0, 0, 3, 0, 4], [0, 0, 5, 7, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 2, 6, 0, 0]]for (var i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++) // Creating Linked List by only those // elements which are non-zero if (sparseMatric[i][j] != 0) { s.create_new_node(i, j, sparseMatric[i][j]) s.data = sparseMatric[i][j] }
// Printing the Linked List Representation// of the sparse matrix
s.PrintList() |
行位置:0 0 1 1 3 3 列位置:2 4 2 3 1 2 值:3 4 5 7 2 6
时间复杂度:
O(N*M),其中N是稀疏矩阵中的行数,M是稀疏矩阵中的列数。
辅助空间:
O(K),其中 K 是数组中非零元素的数量。
其他表示:
作为 字典 ,其中行号和列号用作键,值是矩阵条目。 此方法节省空间,但顺序访问项目的成本较高。
作为
列表的列表
。
这个想法是创建一个行列表,列表中的每个项目都包含值。
我们可以保持列表项按列号排序。
稀疏矩阵及其表示|
第 2 组(使用列表列表和键字典)
如果您喜欢 图码 并愿意做出贡献,您还可以使用 write.geeksforgeeks.org 撰写文章或将您的文章邮寄至 review-team@geeksforgeeks.org。 查看您的文章出现在 图码 主页上并帮助其他极客。