正在载入交互式动画窗口请稍等
基数排序 可视化交互式动画版

基数排序 是一种线性排序算法,通过逐位处理元素来对元素进行排序。 它是一种针对具有固定大小键的整数或字符串的高效排序算法。
基数排序不是直接比较元素,而是根据每个数字的值将元素分配到桶中。 通过按有效数字重复对元素进行排序(从最低有效位到最高有效位),基数排序实现了最终的排序顺序。
基数排序算法
基数排序背后的关键思想是利用位值的概念。 它假设对数字进行逐位排序最终将得到一个完全排序的列表。 可以使用不同的变体来执行基数排序,例如最低有效数字 (LSD) 基数排序或最高有效数字 (MSD) 基数排序。
基数排序算法如何工作?
要对数组 [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66] 执行基数排序,我们按照以下步骤操作:

基数排序算法如何工作? 步骤1
步骤1: 找到数组中最大的元素,即802。它有三位数字,因此我们将迭代三次,每个有效位置一次。
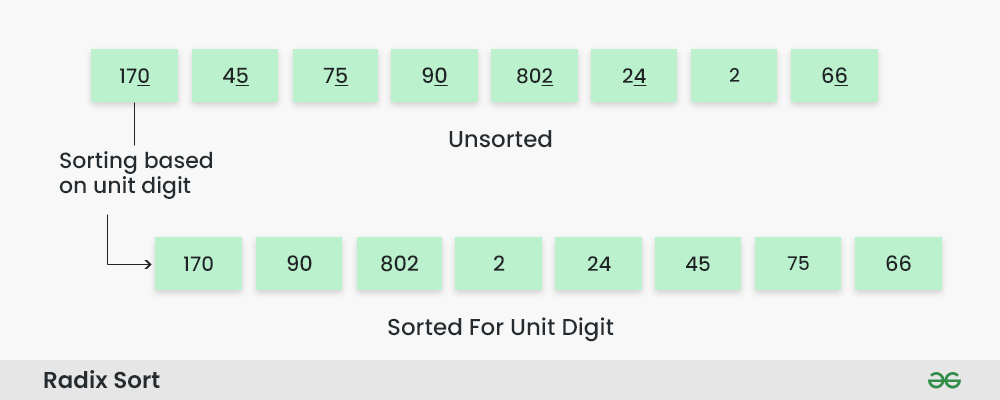
步骤2: 根据个位数字(X=0)对元素进行排序。 我们使用稳定的排序技术,例如计数排序,对每个有效位置的数字进行排序。
按单位位置排序:
- 根据个位数字对数组进行计数排序。
- 基于个位排序的数组为[170, 90, 802, 2, 24, 45, 75, 66]。
基数排序算法如何工作? 第2步
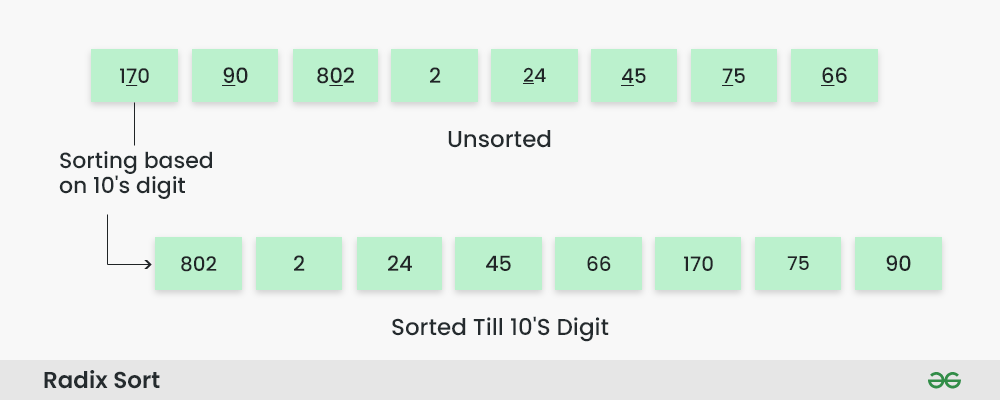
步骤3: 根据十位数字对元素进行排序。
按十位排序:
- 根据十位数字对数组进行计数排序。
- 按十位排序的数组为[802,2,24,45,66,170,75,90]。
基数排序算法如何工作? 步骤3
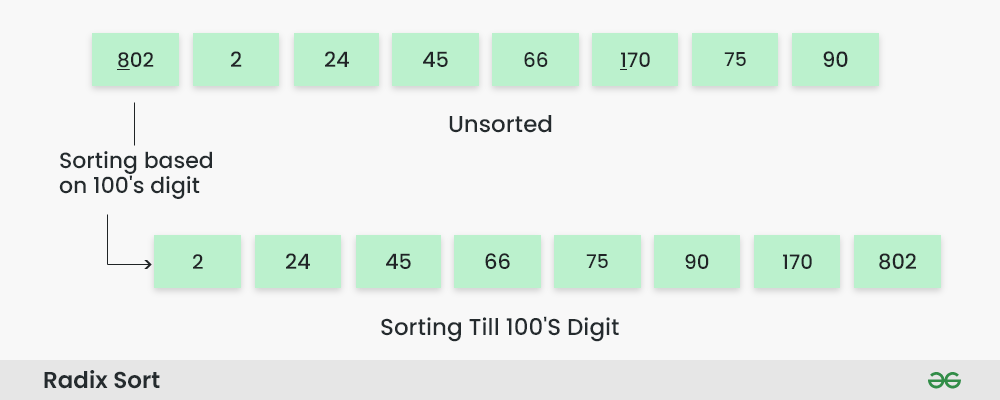
步骤4: 根据百位数字对元素进行排序。
按百位排序:
- 根据百位数字对数组进行计数排序。
- 按百位排序的数组为[2, 24, 45, 66, 75, 90, 170, 802]。
基数排序算法如何工作? 步骤4
步骤5: 现在数组已按升序排序。
使用基数排序的最终排序数组为 [2, 24, 45, 66, 75, 90, 170, 802]。

基数排序算法如何工作? 步骤5
下面是上面插图的实现:
- C++
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
- PHP
C++
// C++ implementation of Radix Sort#include <iostream>using namespace std;// A utility function to get maximum// value in arr[]int getMax(int arr[], int n){ int
mx = arr[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] > mx) mx = arr[i]; return mx;}// A function to do counting sort of arr[]// according to the digit
// represented by exp.
void countSort(int arr[], int n, int exp){ // Output array int
output[n]; int
i, count[10] = { 0 }; // Store count of occurrences // in count[] for (i = 0; i < n; i++) count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++; // Change count[i] so that count[i] // now contains actual position // of this digit in output[] for (i = 1; i < 10; i++) count[i] += count[i - 1]; // Build the output array for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i]; count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--; } // Copy the output array to arr[], // so that arr[] now contains sorted // numbers according to current digit for (i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = output[i];}// The main function to that sorts arr[]// of size n using Radix Sortvoid radixsort(int arr[], int n){ // Find the maximum number to // know number of digits int
m = getMax(arr, n); // Do counting sort for every digit. // Note that instead of passing digit // number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i // where i is current digit number for (int exp = 1; m / exp > 0; exp *= 10) countSort(arr, n, exp);}// A utility function to print an arrayvoid print(int arr[], int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << arr[i] << " ";}// Driver Codeint main(){ int
arr[] = { 543, 986, 217, 765, 329 }; int
n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); // Function Call radixsort(arr, n); print(arr, n); return 0;} |
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
PHP
217 329 543 765 986
基数排序的复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:
- 基数排序是一种非比较整数排序算法,它通过按共享相同有效位置和值的各个数字对键进行分组,对具有整数键的数据进行排序。 它的时间复杂度为 O(d * (n + b)) ,其中 d 是位数,n 是元素数量,b 是所使用的数字系统的基数。
- 在实际实现中,对于大型数据集,基数排序通常比其他基于比较的排序算法(例如快速排序或合并排序)更快,尤其是当键有很多数字时。 然而,它的时间复杂度随着位数线性增长,因此对于小数据集来说效率不高。
辅助空间:
- 基数排序的空间复杂度也为 O(n + b), 其中 n 是元素的数量,b 是数字系统的基数。 这种空间复杂性来自于需要为每个数字值创建存储桶,并在每个数字排序后将元素复制回原始数组。
关于 RadixSort 的常见问题
Q1. 基数排序是否优于快速排序等基于比较的排序算法?
如果每个数字都有 log 2 n 位,那么对于大范围的输入数字,Radix 的运行时间似乎比快速排序要好。 对于基数排序来说,渐近符号中隐藏的常数因子更高,快速排序可以更有效地使用硬件缓存。 此外,基数排序使用计数排序作为子例程,并且计数排序需要额外的空间来对数字进行排序。
Q2。 如果元素在 1 到 n 2 范围内怎么办?
- 基于比较的排序算法(合并排序、堆排序、快速排序等)的下限是 Ω(nLogn),即它们不能比 nLogn 做得更好。 计数排序是一种线性时间排序算法,当元素在 1 到 k 范围内时,排序时间为 O(n+k)。
-
我们不能使用计数排序,因为计数排序将花费 O(n
2
),这比基于比较的排序算法更糟糕。
我们可以在线性时间内对这样的数组进行排序吗?
- 答案是 基数排序。 基数排序的思想是从最低有效数字开始到最高有效数字进行逐位排序。 基数排序使用计数排序作为排序的子例程。