正在载入交互式动画窗口请稍等
快速排序 可视化交互式动画版

QuickSort 是一种基于 分而治之算法 的排序算法,它选择一个元素作为主元,并通过将主元放置在已排序数组中的正确位置,围绕所选主元对给定数组进行分区。
快速排序是如何工作的?
QuickSort 中的关键过程 是 partition() 。 分区的目标是将主元(可以选择任何元素作为主元)放置在已排序数组中的正确位置,并将所有较小的元素放在主元的左侧,将所有较大的元素放在主元的右侧。
将枢轴放置在正确的位置后,在枢轴的每一侧递归地完成分区,最终对数组进行排序。
快速排序的工作原理
枢轴的选择:
选择枢轴有许多不同的选择。
- 始终选择第一个元素作为枢轴 。
- 始终选择最后一个元素作为基准(在下面实现)
- 选择一个随机元素作为基准 。
- 选择中间作为枢轴。
分区算法:
逻辑很简单,我们从最左边的元素开始,并跟踪较小(或等于)元素的索引 i 。 遍历时,如果找到较小的元素,则将当前元素与 arr[i] 交换。 否则,我们忽略当前元素。
让我们借助以下示例来了解分区和快速排序算法的工作原理:
考虑:arr[] = {10, 80, 30, 90, 40}。
- 将10与枢轴比较,小于枢轴则依次排列。
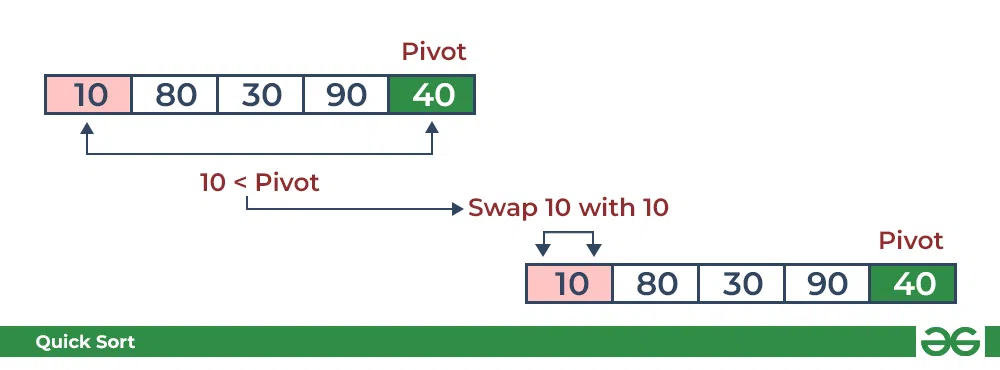
QuickSort 中的分区:将主元与 10 进行比较
- 将 80 与枢轴进行比较。 它大于枢轴。
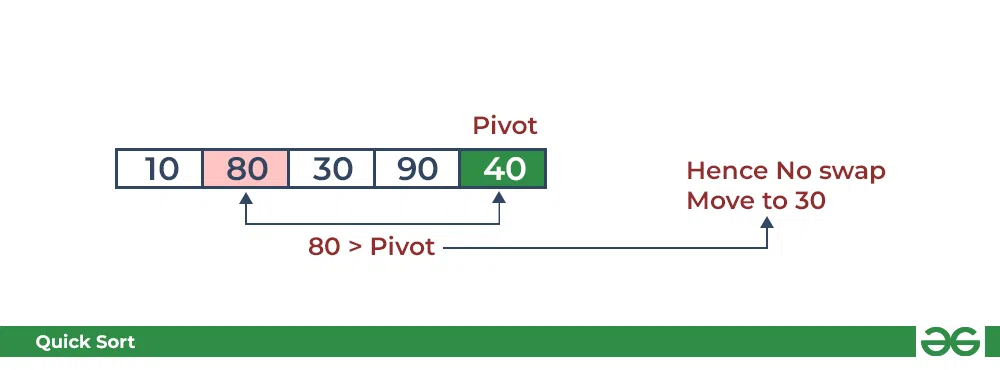
QuickSort 中的分区:将枢轴与 80 进行比较
- 将 30 与枢轴进行比较。 它小于枢轴,因此请相应地安排它。
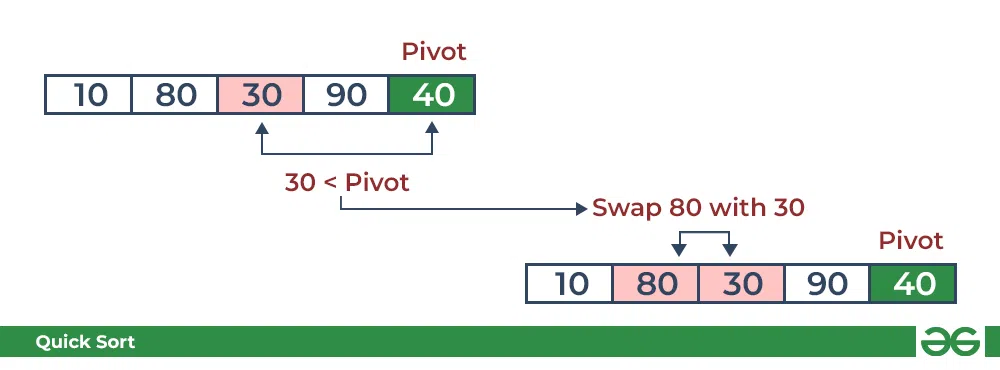
QuickSort 中的分区:将数据透视表与 30 进行比较
- 将 90 与枢轴进行比较。 它大于枢轴。
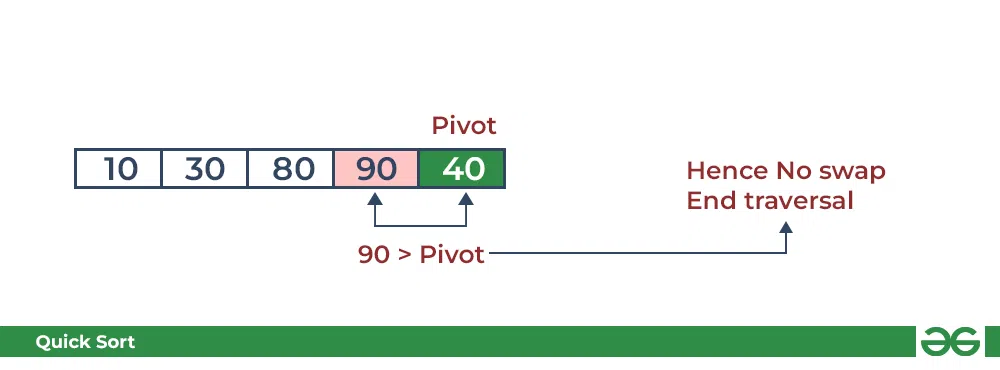
QuickSort 中的分区:将枢轴与 90 进行比较
- 将枢轴布置在正确的位置。
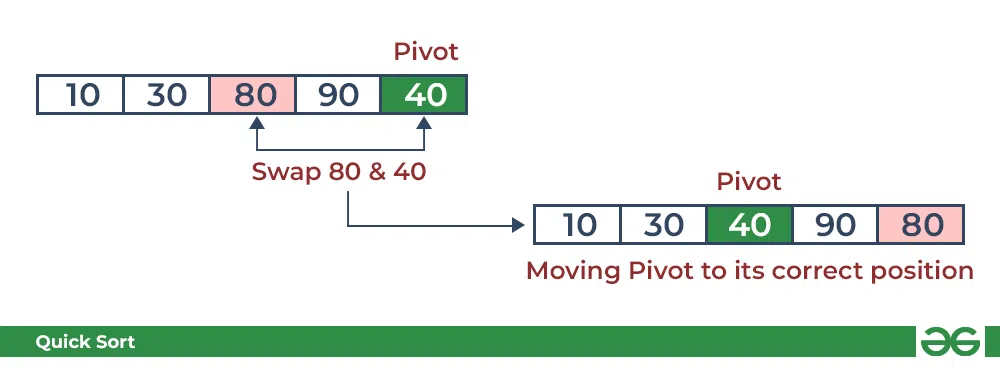
QuickSort 中的分区:将枢轴放置在正确的位置
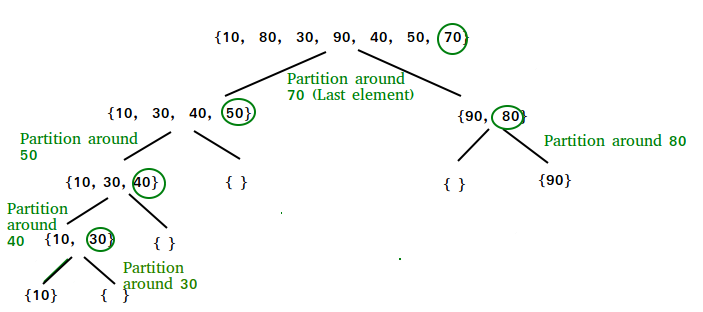
快速排序的说明:
由于分区过程是递归完成的,因此它不断地将主元放在排序数组中的实际位置。 反复将枢轴放入其实际位置可以使数组排序。
按照下图了解分区算法的递归实现如何帮助对数组进行排序。
- 主阵列上的初始分区:
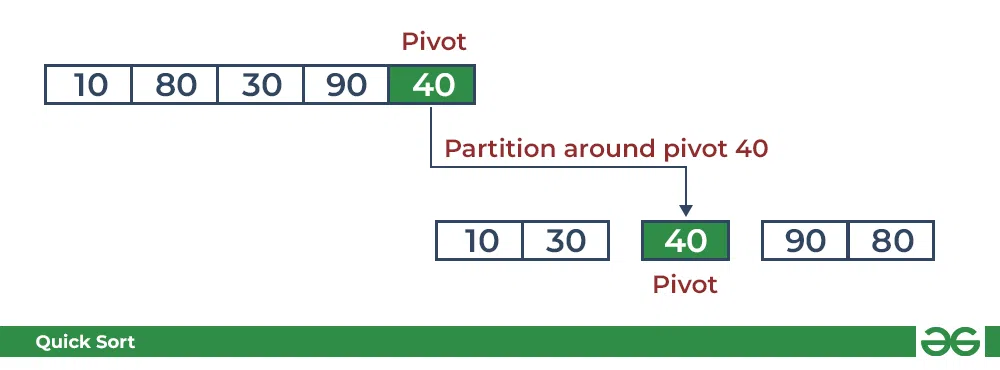
快速排序:执行分区
- 子数组的划分:

快速排序:执行分区
快速排序的代码实现:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int partition(int arr[],int low,int high)
{ //choose the pivot
int pivot=arr[high]; //Index of smaller element and Indicate //the right position of pivot found so far int i=(low-1);
for(int j=low;j<=high;j++) { //If current element is smaller than the pivot if(arr[j]<pivot) { //Increment index of smaller element i++; swap(arr[i],arr[j]); } } swap(arr[i+1],arr[high]); return (i+1);}// The Quicksort function Implement
void quickSort(int arr[],int low,int high)
{ // when low is less than high if(low<high) { // pi is the partition return index of pivot int
pi=partition(arr,low,high); //Recursion Call //smaller element than pivot goes left and //higher element goes right quickSort(arr,low,pi-1); quickSort(arr,pi+1,high); }}
int main() { int arr[]={10,7,8,9,1,5}; int n=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); // Function call quickSort(arr,0,n-1); //Print the sorted array cout<<"Sorted Array\n"; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } return 0;}// This Code is Contributed By Diwakar Jha |
Java
// Java implementation of QuickSortimport java.io.*;class GFG { // A utility function to swap two elements static
void swap(int[] arr, int
i, int j)
{ int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } // This function takes last element as pivot, // places the pivot element at its correct position // in sorted array, and places all smaller to left // of pivot and all greater elements to right of pivot static
int partition(int[] arr, int
low, int high) { // Choosing the pivot int pivot = arr[high]; // Index of smaller element and indicates // the right position of pivot found so far int i = (low - 1); for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if (arr[j] < pivot) { // Increment index of smaller element i++; swap(arr, i, j); } } swap(arr, i + 1, high); return (i + 1); } // The main function that implements QuickSort // arr[] --> Array to be sorted, // low --> Starting index, // high --> Ending index static
void quickSort(int[] arr, int
low, int high) { if (low < high) { // pi is partitioning index, arr[p] // is now at right place int pi = partition(arr, low, high); // Separately sort elements before // partition and after partition quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); } } // To print sorted array public
static void printArr(int[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } // Driver Code public
static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5 }; int N = arr.length; // Function call quickSort(arr, 0, N - 1); System.out.println("Sorted array:"); printArr(arr); }}// This code is contributed by Ayush Choudhary// Improved by Ajay Virmoti
|
Python3
# Python3 implementation of QuickSort# Function to find the partition positiondef partition(array, low, high): # Choose the rightmost element as pivot pivot = array[high] # Pointer for greater element i = low - 1 # Traverse through all elements # compare each element with pivot for j in range(low, high): if array[j] <= pivot: # If element smaller than pivot is found # swap it with the greater element pointed by i i = i + 1 # Swapping element at i with element at j (array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i]) # Swap the pivot element with # the greater element specified by i (array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1]) # Return the position from where partition is done return
i + 1# Function to perform quicksortdef quicksort(array, low, high): if low < high: # Find pivot element such that # element smaller than pivot are on the left # element greater than pivot are on the right pi = partition(array, low, high) # Recursive call on the left of pivot quicksort(array, low, pi - 1) # Recursive call on the right of pivot quicksort(array, pi + 1, high)# Driver codeif __name__ ==
'__main__': array = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5] N = len(array)
# Function call quicksort(array, 0, N - 1) print('Sorted array:') for x in array: print(x, end=" ")# This code is contributed by Adnan Aliakbar |
C#
// C# implementation of QuickSortusing System;class GFG { // A utility function to swap two elements static
void swap(int[] arr, int
i, int j)
{ int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } // This function takes last element as pivot, // places the pivot element at its correct position // in sorted array, and places all smaller to left // of pivot and all greater elements to right of pivot static
int partition(int[] arr, int
low, int high) { // Choosing the pivot int pivot = arr[high]; // Index of smaller element and indicates // the right position of pivot found so far int i = (low - 1); for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if (arr[j] < pivot) { // Increment index of smaller element i++; swap(arr, i, j); } } swap(arr, i + 1, high); return (i + 1); } // The main function that implements QuickSort // arr[] --> Array to be sorted, // low --> Starting index, // high --> Ending index static
void quickSort(int[] arr, int
low, int high) { if (low < high) { // pi is partitioning index, arr[p] // is now at right place int pi = partition(arr, low, high); // Separately sort elements before // and after partition index quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); } } // Driver Code public
static void Main() { int[] arr = { 10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5 }; int N = arr.Length; // Function call quickSort(arr, 0, N - 1); Console.WriteLine("Sorted array:"); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); }}// This code is contributed by gfgking |
JavaScript
// Function to partition the array and return the partition index
function partition(arr, low, high) { // Choosing the pivot let pivot = arr[high];
// Index of smaller element and indicates the right position of pivot found so far
let i = low - 1;
for (let j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if (arr[j] < pivot) { // Increment index of smaller element i++; [arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]]; // Swap elements } }
[arr[i + 1], arr[high]] = [arr[high], arr[i + 1]]; // Swap pivot to its correct position return
i + 1; // Return the partition index
}// The main function that implements QuickSortfunction quickSort(arr, low, high) { if (low < high) { // pi is the partitioning index, arr[pi] is now at the right place
let pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Separately sort elements before partition and after partition quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); }}// Driver codelet arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5];
let N = arr.length;// Function callquickSort(arr, 0, N - 1);console.log("Sorted array:");console.log(arr.join(" ")); |
PHP
<?php
// This Function takes place last element as pivot // Place the pivot as correct position // In Sorted Array, and places all smaller to left // of pivot and all greater element to its right of pivot
function partition(&$arr,$low,$high) { // Choose the Pivot Element $pivot= $arr[$high]; // Index of smaller element and indicates // The right position of pivot $i=($low-1); for($j=$low;$j<=$high-1;$j++) { if($arr[$j]<$pivot) { // Increment index of smaller element $i++; list($arr[$i],$arr[$j])=array($arr[$j],$arr[$i]); } } // Pivot element as correct position list($arr[$i+1],$arr[$high])=array($arr[$high],$arr[$i+1]); return
($i+1);
}// The main function that implement as QuickSort// arr[]:- Array to be sorted// low:- Starting Index
//high:- Ending Indexfunction quickSort(&$arr,$low,$high){ if($low<$high) { // pi is partition $pi= partition($arr,$low,$high); // Sort the array // Before the partition of Element quickSort($arr,$low,$pi-1); // After the partition Element quickSort($arr,$pi+1,$high); }}// Driver Code$arr= array(10,7,8,9,1,5);$N=count($arr);// Function CallquickSort($arr,0,$N-1);echo "Sorted Array:\n";for($i=0;$i<$N;$i++){ echo $arr[$i]. " ";} //This code is contributed by Diwakar Jha?> |
排序数组: 1 5 7 8 9 10
快速排序的复杂度分析 :
时间复杂度:
-
最佳情况
:Ω (N log (N))
快速排序的最佳情况发生在每一步选择的主元将数组分成大致相等的两半时。
在这种情况下,算法将进行平衡分区,从而实现高效排序。 -
平均情况:θ ( N log (N))
快速排序的平均情况性能在实践中通常非常好,使其成为最快的排序算法之一。
-
最坏情况:O(N2)
快速排序的最坏情况发生在每一步的枢轴始终导致高度不平衡的分区时。
当数组已经排序并且枢轴始终被选为最小或最大元素时。
为了缓解最坏的情况,使用了各种技术,例如选择一个好的主元(例如,三的中位数)并使用随机算法(随机快速排序)在排序之前对元素进行混洗。
- 辅助空间: 如果不考虑递归栈空间,O(1)。 如果我们考虑递归堆栈空间,那么在最坏的情况下,快速排序的时间复杂度可能是 O ( N )。
快速排序的优点:
- 它是一种分而治之的算法,可以更轻松地解决问题。
- 它在大型数据集上非常有效。
- 它的开销很低,因为它只需要少量的内存即可运行。
快速排序的缺点:
- 它的最坏情况时间复杂度为 O(N 2 ),当主元选择不当时就会发生这种情况。
- 对于小数据集来说这不是一个好的选择。
- 它不是稳定的排序,这意味着如果两个元素具有相同的键,在快速排序的情况下,它们的相对顺序将不会保留在排序输出中,因为这里我们根据枢轴的位置交换元素(不考虑它们的原始位置)职位)。