正在载入交互式动画窗口请稍等
循环双链表 可视化交互式动画版

循环双向链表具有 双向链表 和 循环链表 的性质,其中两个连续的元素通过前一个和后一个指针链接或连接,最后一个节点通过下一个指针指向第一个节点,第一个节点也指向前一个指针的最后一个节点。
以下是循环双向链表节点在 C/C++ 中的表示:
- C++
- C
- Java
- Python
- C#
C++
static class node { int data; // pointer to next node node next; // pointer to prev node node prev;}
// This code is contributed by Yash Agarwal(yashagarwal2852002)
|
C
Java
Python
C#
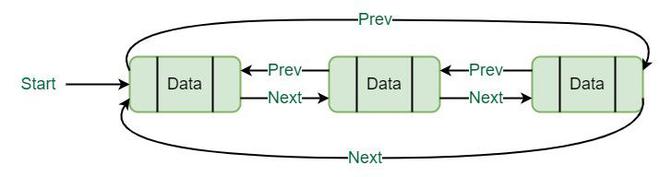
循环双向链表
插入循环双向链表:
1. 在列表末尾或空列表中插入:
插入 一个节点(比如 N ), 数据 = 5 。 所以,N的前一个指针指向N,N的下一个指针也指向N。但是现在start指针指向链表的第一个节点。
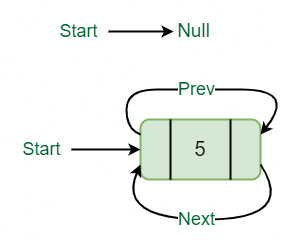
插入空列表
2. List最初包含一些节点,start指向List的第一个节点:
插入一个节点(假设M),其data = 7,因此M的前一个指针指向最后一个节点,M的下一个指针指向第一个节点,最后一个节点的next指针指向这个M节点,而第一个节点的next指针指向第一个节点。 previous指针指向这个M节点。
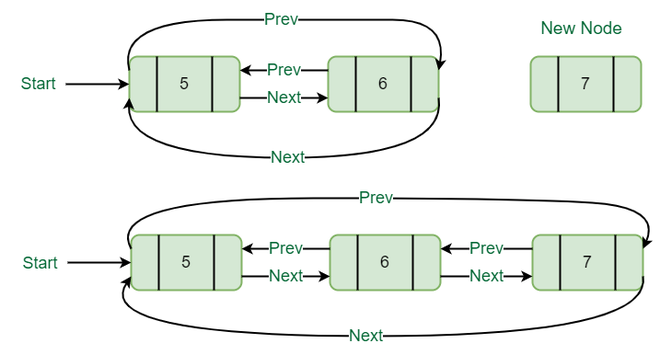
在列表末尾插入
下面是上述操作的实现:
- C++
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
C++
// Function to insert at the endvoid insertEnd(struct Node** start, int value){ // If the list is empty, create a single node // circular and doubly list if (*start == NULL) { struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value; new_node->next = new_node->prev = new_node; *start = new_node; return; } // If list is not empty /* Find last node */ Node* last = (*start)->prev; // Create Node dynamically struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value; // Start is going to be next of new_node new_node->next = *start; // Make new node previous of start (*start)->prev = new_node; // Make last previous of new node new_node->prev = last; // Make new node next of old last last->next = new_node;} |
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
3. 在列表开头插入:
要在链表的开头插入一个节点,请创建一个数据 = 5 的节点(例如 T),T next 指针指向链表的第一个节点,T previous 指针指向链表的最后一个节点,最后一个节点的下一个节点指针指向这个T节点,第一个节点的前一个指针也指向这个T节点,最后不要忘记将“Start”指针移到这个T节点。
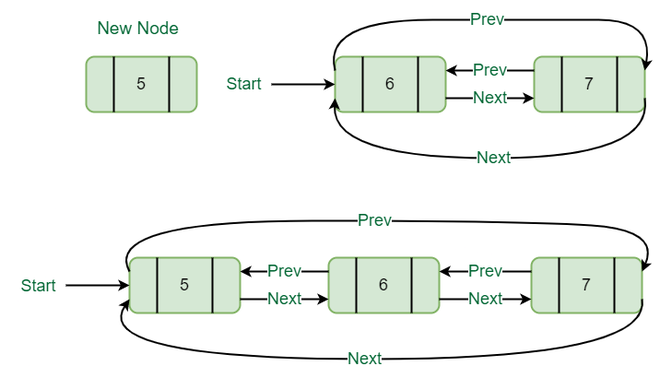
在列表开头插入
下面是上述操作的实现:
- C++
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
C++
// Function to insert Node at the beginning// of the List,void insertBegin(struct Node** start, int value){ // Pointer points to last Node struct Node* last = (*start)->prev; struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value; // Inserting the data // setting up previous and next of new node new_node->next = *start; new_node->prev = last; // Update next and previous pointers of start // and last. last->next = (*start)->prev = new_node; // Update start pointer *start = new_node;} |
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
4. 在列表的节点之间插入 :
要在列表之间插入节点,需要两个数据值,一个数据值将插入新节点,另一个数据值是新节点的数据。
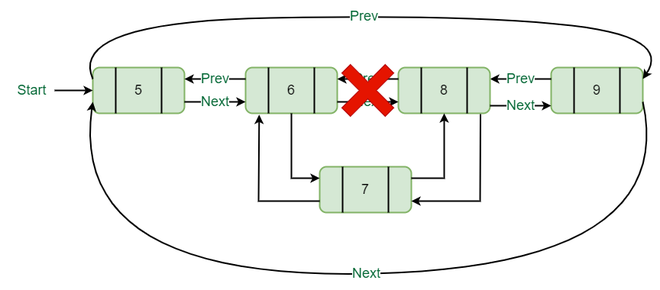
插入其他节点之间
下面是上述操作的实现:
- C++
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
C++
// Function to insert node with value as value1.// The new node is inserted after the node with// with value2void insertAfter(struct Node** start, int value1, int value2){ struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value1; // Inserting the data // Find node having value2 and next node of it struct Node* temp = *start; while (temp->data != value2)
temp = temp->next; struct Node* next = temp->next;
// insert new_node between temp and next. temp->next = new_node; new_node->prev = temp; new_node->next = next; next->prev = new_node;} |
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
以下是一个完整的程序,它使用上述所有方法来创建一个循环双向链表。
- C++
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
C++
// C++ program to illustrate inserting a Node in// a Circular Doubly Linked list in begging, end// and middle#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// Structure of a Nodestruct Node { int
data; struct Node* next; struct Node* prev;};// Function to insert at the endvoid insertEnd(struct Node** start, int value){ // If the list is empty, create a single node // circular and doubly list if
(*start == NULL) { struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value; new_node->next = new_node->prev = new_node; *start = new_node; return; } // If list is not empty /* Find last node */ Node* last = (*start)->prev; // Create Node dynamically struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value; // Start is going to be next of new_node new_node->next = *start; // Make new node previous of start (*start)->prev = new_node; // Make last previous of new node new_node->prev = last; // Make new node next of old last last->next = new_node;}// Function to insert Node at the beginning// of the List,void insertBegin(struct Node** start, int value){ // Pointer points to last Node struct Node* last = (*start)->prev; struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value; // Inserting the data // setting up previous and next of new node new_node->next = *start; new_node->prev = last; // Update next and previous pointers of start // and last. last->next = (*start)->prev = new_node; // Update start pointer *start = new_node;}// Function to insert node with value as value1.// The new node is inserted after the node with// with value2void insertAfter(struct Node** start, int value1, int value2){ struct Node* new_node = new Node; new_node->data = value1; // Inserting the data // Find node having value2 and next node of it struct Node* temp = *start; while (temp->data != value2) temp = temp->next; struct Node* next = temp->next;
// insert new_node between temp and next. temp->next = new_node; new_node->prev = temp; new_node->next = next; next->prev = new_node;}void display(struct Node* start){ struct Node* temp = start; printf("\nTraversal in forward direction \n");
while (temp->next != start) {
printf("%d ", temp->data); temp = temp->next; } printf("%d ", temp->data); printf("\nTraversal in reverse direction \n");
Node* last = start->prev; temp = last; while (temp->prev != last) { printf("%d ", temp->data); temp = temp->prev; } printf("%d ", temp->data);}/* Driver program to test above functions*/int main(){ /* Start with the empty list */ struct Node* start = NULL; // Insert 5. So linked list becomes 5->NULL insertEnd(&start, 5); // Insert 4 at the beginning. So linked // list becomes 4->5 insertBegin(&start, 4); // Insert 7 at the end. So linked list // becomes 4->5->7 insertEnd(&start, 7); // Insert 8 at the end. So linked list // becomes 4->5->7->8 insertEnd(&start, 8); // Insert 6, after 5. So linked list // becomes 4->5->6->7->8 insertAfter(&start, 6, 5); printf("Created circular doubly linked list is: "); display(start); return 0;} |
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
创建的循环双向链表为: 向前移动 4 5 6 7 8 反向遍历 8 7 6 5 4
时间复杂度:
O(N)
辅助空间:
O(1),使用恒定的额外空间。
循环双向链表的优点:
- 该列表可以从两个方向遍历,即从头到尾或从尾到头。
- 从头跳到尾或从尾跳到头的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
- 循环双向链表用于实现 斐波那契堆 等高级数据结构。
循环双向链表的缺点:
- 每个节点需要稍微额外的内存来容纳前一个指针。
- 在列表上实现或执行操作时涉及到许多指针。 因此,应该小心处理指针,否则列表的数据可能会丢失。
循环双向链表的应用:
- 管理媒体播放器应用程序中的歌曲播放列表。
- 管理在线购物中的购物车。
本文由 阿卡什·古普塔贡 献。 如果您喜欢 图码 并愿意做出贡献,您还可以使用 write.geeksforgeeks.org 撰写文章或将您的文章邮寄至 review-team@geeksforgeeks.org。 查看您的文章出现在 图码 主页上并帮助其他极客。