正在载入交互式动画窗口请稍等
折半查找 可视化交互式动画版

二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search) 被定义为一种 在排序数组中使用的 搜索算法,通过 重复将搜索间隔一分为二 。 二分查找的思想是利用数组已排序的信息,将时间复杂度降低到O(log N)。
二分查找算法示例
何时在数据结构中应用二分查找的条件:
应用二分查找算法:
- 数据结构必须是有序的。
- 访问数据结构的任何元素都需要恒定的时间。
二分查找算法:
在这个算法中,
- 通过查找中间索引“mid” 将搜索空间分为两半 。

在二分查找算法中查找中间索引“mid”
- 将搜索空间的中间元素与键进行比较。
- 如果在中间元素找到密钥,则过程终止。
- 如果在中间元素没有找到键,则选择哪一半将用作下一个搜索空间。
- 如果键小于中间元素,则使用左侧进行下一步搜索。
- 如果键大于中间元素,则使用右侧进行下一步搜索。
- 这个过程一直持续到找到密钥或者总搜索空间耗尽为止。
二分查找如何工作?
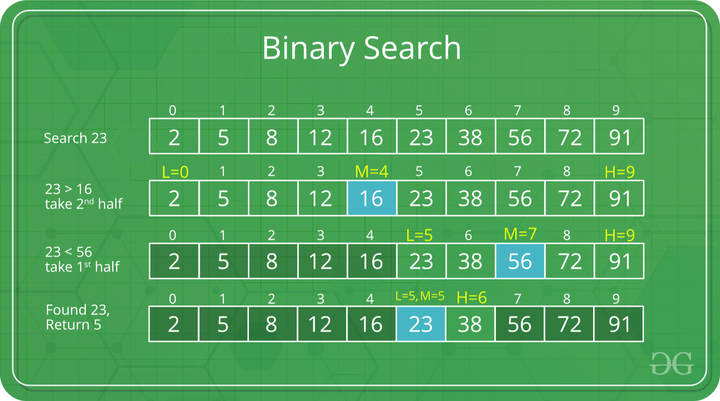
要了解二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search)的工作原理,请考虑下图:
考虑一个数组 arr[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91} , 目标 = 23 。
第一步: 计算mid并将mid元素与key进行比较。 如果键小于 mid 元素,则向左移动,如果大于 mid 则将搜索空间向右移动。
- 键(即 23)大于当前中间元素(即 16)。 搜索空间向右移动。

二分查找算法:将键与 16 进行比较
- 密钥小于当前的中间 56。搜索空间向左移动。

二分查找算法:将键与 56 进行比较
第二步: 如果key与mid元素的值匹配,则找到该元素并停止搜索。

二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search)算法:与 mid 的关键匹配
如何实现二分查找?
二分查找算法 可以 通过以下两种方式实现
- 迭代二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search)算法
- 递归二分查找算法
下面给出了这些方法的伪代码。
1.迭代二分查找算法:
这里我们使用 while 循环来继续比较键并将搜索空间分成两半的过程。
迭代二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search)算法的实现:
- C++
- C
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
- PHP
C++
// C++ program to implement iterative Binary Search#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// An iterative binary search function.int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{ while (l <= r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Check if x is present at mid if (arr[m] == x) return m; // If x greater, ignore left half if (arr[m] < x) l = m + 1; // If x is smaller, ignore right half else r = m - 1; } // If we reach here, then element was not present return -1;}// Driver codeint main(void)
{ int
arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 }; int
x = 10; int
n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x); (result == -1) ? cout << "Element is not present in array" : cout << "Element is present at index " << result; return 0;} |
C
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
PHP
元素出现在索引 3 处
时间复杂度:
O(log N)
辅助空间:
O(1)
2.递归二分查找算法:
创建一个递归函数并将搜索空间的中间部分与键进行比较。 并根据结果返回找到键的索引或调用下一个搜索空间的递归函数。
递归二分查找算法的实现:
- C++
- C
- Java
- Python3
- C#
- JavaScript
- PHP
C++
// C++ program to implement recursive Binary Search#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// A recursive binary search function. It returns// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,// otherwise -1int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{ if
(r >= l) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // If the element is present at the middle // itself if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; // If element is smaller than mid, then // it can only be present in left subarray if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); // Else the element can only be present // in right subarray return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } // We reach here when element is not // present in array return -1;}// Driver codeint main(){ int
arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 }; int
x = 10; int
n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x); (result == -1) ? cout << "Element is not present in array" : cout << "Element is present at index " << result; return 0;} |
C
Java
Python3
C#
JavaScript
PHP
元素出现在索引 3 处
二分查找的复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:
- 最佳情况:O(1)
- 平均情况:O(log N)
- 最坏情况:O(log N)
- 辅助空间: O(1),如果考虑递归调用栈则辅助空间为O(logN)。
二分查找的优点:
- 二分查找比线性查找更快,特别是对于大型数组。
- 比具有类似时间复杂度的其他搜索算法(例如插值搜索或指数搜索)更有效。
- 二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search)非常适合搜索存储在外部存储器(例如硬盘驱动器或云中)中的大型数据集。
二分查找的缺点:
- 数组应该是排序的。
- 二分查找要求将要查找的数据结构存储在连续的内存位置中。
- 二分查找要求数组的元素是可比较的,这意味着它们必须能够排序。
二分查找的应用:
- 二分搜索折半查找(Binary Search)可以用作机器学习中使用的更复杂算法的构建块,例如训练神经网络或查找模型的最佳超参数的算法。
- 它可用于计算机图形学中的搜索,例如光线追踪或纹理映射的算法。
- 它可用于搜索数据库。